Introduction
Picture this: It's 2 AM in a major distribution center, and a critical shipment arrives six hours ahead of schedule. Simultaneously, three conveyor belts show early signs of mechanical stress, inventory counts reveal unexpected discrepancies in high-demand SKUs, and the morning shift is down two workers due to illness. In traditional warehouses, these converging challenges would trigger a cascade of manual interventions, delayed decisions, and potential customer disappointments.
This is where agentic AI transforms the game. Unlike traditional automation that follows rigid scripts, agentic AI systems can perceive, reason, decide, and act autonomously—adapting to complex, dynamic situations in real-time. Google Cloud's Vertex AI platform combined with Gemini, their most advanced multimodal AI model, represents the cutting edge of this transformation.
Vertex AI provides the infrastructure for building, deploying, and scaling machine learning models, while Gemini brings unprecedented reasoning capabilities across text, images, video, and code. Together, they create AI agents that don't just automate tasks—they understand context, make intelligent decisions, and continuously learn from every interaction. For warehouse operations facing unprecedented pressure to do more with less, this technology stack isn't just an upgrade—it's a fundamental reimagining of what's possible.
Current Warehouse Challenges
Modern warehouse operations face a perfect storm of challenges that traditional technology struggles to address. Labor shortages have reached crisis levels, with the logistics industry experiencing turnover rates exceeding 40% in some regions. The cost of constantly recruiting and training new workers drains resources while institutional knowledge walks out the door.
Real-time decision-making complexity has exploded as e-commerce drives demand for same-day delivery and customers expect perfect order accuracy. Managers must simultaneously optimize for speed, cost, accuracy, and worker safety across hundreds of variables that change by the minute.
Data silos remain a persistent problem. Your WMS knows inventory levels, your ERP tracks orders, your IoT sensors monitor equipment, and your TMS manages transportation—but these systems rarely communicate effectively. Critical insights remain trapped in disconnected databases, preventing holistic optimization.
Inventory accuracy and visibility issues cost the industry billions annually. Physical counts diverge from system records, leading to stockouts of available items and overstocking of slow movers. Without real-time visibility into actual conditions, warehouses operate partially blind.
The need for predictive and adaptive operations has never been greater. Reactive management—addressing problems after they occur—is no longer competitive. Modern warehouses must anticipate demand spikes, predict equipment failures before they happen, and dynamically adjust operations based on real-time conditions.
Finally, scalability demands during peak seasons stress every system. Black Friday, Prime Day, and holiday rushes require warehouses to handle 3-5x normal volume without proportionally increasing costs or errors. Traditional systems scale linearly—more volume requires more people, more space, more time. That math no longer works.
Understanding the Technology Stack
Vertex AI: Google Cloud's Unified AI Platform
Vertex AI is Google Cloud's comprehensive platform for building, deploying, and scaling machine learning solutions. Think of it as your AI development and operations headquarters, providing everything needed to move from raw data to production-ready intelligent systems.
Machine learning model development and deployment on Vertex AI happens through a unified workflow. Data scientists can experiment with models using pre-built algorithms or custom code, then deploy those models to managed prediction endpoints with enterprise-grade reliability. The platform handles infrastructure scaling automatically, so your demand forecasting model that predicts next week's orders runs with the same reliability whether processing 1,000 or 1,000,000 predictions.
AutoML capabilities democratize AI by enabling teams without deep data science expertise to build custom models. Upload your historical shipment data, define what you want to predict, and AutoML automatically tests hundreds of model architectures to find the best performer. This means your warehouse operations team can build specialized models for their unique challenges without waiting months for data science resources.
Model monitoring and management ensures your AI systems maintain accuracy over time. Vertex AI continuously tracks prediction quality, data drift, and model performance. When your inventory forecasting model's accuracy begins to slip—perhaps because supplier lead times have changed—the platform alerts you and simplifies retraining with fresh data.
Gemini: Google's Multimodal AI Model
Gemini represents a fundamental leap in AI capabilities, understanding and generating content across text, images, video, code, and audio within a single model. For warehouse operations, this multimodality is transformative.
Text, image, and video understanding capabilities mean Gemini can simultaneously read a shipping manifest, examine a photo of damaged packaging, and analyze security camera footage showing how the damage occurred. Traditional AI systems require separate models for each data type; Gemini processes them together, understanding relationships and context that would be invisible to isolated systems.
Reasoning and decision-making abilities set Gemini apart from simpler AI models. When asked to optimize picking routes, Gemini doesn't just calculate shortest paths—it considers worker fatigue patterns, understands that certain product combinations indicate gift orders requiring special care, and reasons about trade-offs between speed and accuracy based on customer priority levels.
Integration with enterprise systems is straightforward through APIs that support both synchronous and streaming responses. Your WMS can query Gemini in real-time, receiving intelligent responses within milliseconds for time-critical decisions or using longer processing for complex optimization problems.
Why This Combination Powers Agentic AI
The synergy between Vertex AI and Gemini creates truly agentic systems through three key capabilities:
Autonomous decision-making emerges when Gemini's reasoning abilities run on Vertex AI's scalable infrastructure. An agent monitoring receiving dock operations can analyze camera feeds of incoming pallets, read shipping documents, consult inventory databases, and automatically direct fork-lift operators to optimal put-away locations—all without human intervention.
Continuous learning and adaptation happens as Vertex AI tracks every decision's outcome and retrains models with fresh data. When your quality control agent initially flags 15% false positives, it learns from corrections and improves to 99% accuracy over weeks, adapting to your specific products and standards.
Multi-modal data processing allows agents to operate in the messy real world where information arrives as text messages, images, sensor readings, voice commands, and video simultaneously. A single agent can coordinate receiving (video inspection), inventory updates (database writes), quality documentation (image capture with text annotations), and exception handling (natural language messages to supervisors).
Agentic AI Applications Using Vertex AI and Gemini
A. Intelligent Inventory Management
Traditional inventory systems react to depleted stock; agentic AI anticipates needs and optimizes placement dynamically.
Vertex AI for demand forecasting leverages time-series models that analyze historical sales, seasonal patterns, marketing calendars, and external factors like weather or economic indicators. Here's a practical implementation:
from google.cloud import aiplatform
from google.cloud.aiplatform import gapic
import pandas as pd
# Initialize Vertex AI
aiplatform.init(project='your-warehouse-project', location='us-central1')
# Create a forecasting dataset
def create_forecast_dataset(sku_data):
"""
Prepare time-series data for demand forecasting
sku_data: DataFrame with columns [timestamp, sku, quantity_sold, promotions, weather]
"""
dataset = aiplatform.TimeSeriesDataset.create(
display_name='warehouse_demand_forecast',
gcs_source='gs://your-bucket/inventory-history.csv',
column_specs={
'timestamp': 'time',
'sku': 'time_series_identifier',
'quantity_sold': 'target',
'promotions': 'covariate',
'weather_temp': 'covariate'
}
)
return dataset
# Train a forecasting model
def train_demand_model(dataset):
model = aiplatform.AutoMLForecastingTrainingJob(
display_name='sku_demand_forecaster',
optimization_objective='minimize-rmse',
forecast_horizon=14, # Predict 14 days ahead
data_granularity_unit='day',
data_granularity_count=1
)
model.run(
dataset=dataset,
target_column='quantity_sold',
time_column='timestamp',
time_series_identifier_column='sku',
budget_milli_node_hours=3000
)
return model
# Deploy for real-time predictions
def deploy_forecast_endpoint(model):
endpoint = model.deploy(
machine_type='n1-standard-4',
min_replica_count=1,
max_replica_count=10,
traffic_split={"0": 100}
)
return endpoint
# Get predictions for restocking
def get_restock_predictions(endpoint, sku_list):
predictions = endpoint.predict(instances=[
{"sku": sku, "days_ahead": 14}
for sku in sku_list
])
restock_needed = []
for pred in predictions.predictions:
if pred['forecast'] > current_stock(pred['sku']) * 1.2:
restock_needed.append({
'sku': pred['sku'],
'predicted_demand': pred['forecast'],
'confidence': pred['confidence_interval']
})
return restock_needed
Gemini for analyzing unstructured data adds context that numerical models miss. Supplier emails mentioning production delays, social media trends indicating viral products, or news about competitor stockouts all influence demand but exist as unstructured text.
import vertexai
from vertexai.generative_models import GenerativeModel, Part
def analyze_supplier_communications(email_thread):
"""
Use Gemini to extract actionable inventory insights from supplier emails
"""
vertexai.init(project='your-warehouse-project', location='us-central1')
model = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
prompt = f"""
Analyze this supplier email thread and extract inventory-relevant information:
Email Thread:
{email_thread}
Provide a structured response with:
1. Any mentioned delivery delays or expedited shipments
2. Product availability changes
3. Quality issues reported
4. Recommended actions for inventory planning
Format as JSON.
"""
response = model.generate_content(prompt)
return response.text
# Example integration with inventory system
def intelligent_reorder_decision(sku):
"""
Combine Vertex AI forecasts with Gemini context analysis
"""
# Get numerical forecast
forecast = forecast_endpoint.predict(instances=[{"sku": sku}])
# Get contextual insights
supplier_emails = get_recent_supplier_emails(sku)
context = analyze_supplier_communications(supplier_emails)
# Get market sentiment
market_data = fetch_market_trends(sku)
sentiment_prompt = f"""
Based on this market data: {market_data}
And forecast: {forecast}
And supplier context: {context}
Should we adjust our standard reorder quantity? Consider:
- Risk of stockout vs excess inventory
- Supplier reliability signals
- Market momentum
Provide recommendation with confidence level.
"""
recommendation = model.generate_content(sentiment_prompt)
return recommendation.text
Dynamic reordering and stock optimization happens continuously as the agent monitors all data sources, updating reorder points and safety stock levels based on evolving conditions.
Visual inventory recognition using Gemini's vision capabilities enables physical inventory auditing without manual scanning:
def visual_inventory_audit(camera_feed_images):
"""
Use Gemini to count and verify inventory from camera images
"""
model = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
results = []
for shelf_image in camera_feed_images:
# Load image
image_part = Part.from_uri(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
uri=f"gs://warehouse-cameras/{shelf_image}"
)
prompt = """
Analyze this warehouse shelf image:
1. Count the number of boxes visible on each shelf level
2. Identify any SKU labels visible and their quantities
3. Note any obvious discrepancies (damaged boxes, disorganization, wrong items)
4. Compare to expected layout if provided in metadata
Return structured JSON with counts and discrepancies.
"""
response = model.generate_content([image_part, prompt])
results.append(response.text)
return consolidate_audit_results(results)
B. Autonomous Task Orchestration
Warehouse efficiency depends on assigning the right tasks to the right people at the right time. Agentic AI excels at this dynamic optimization.
Real-time work assignment using Vertex AI prediction models considers worker skills, location, fatigue levels, and task urgency:
from google.cloud import aiplatform
import numpy as np
class TaskOrchestrationAgent:
def __init__(self, endpoint_name):
self.endpoint = aiplatform.Endpoint(endpoint_name)
self.active_tasks = []
self.worker_status = {}
def optimize_task_assignment(self, pending_tasks, available_workers):
"""
Use ML model to predict optimal task-worker assignments
"""
# Prepare features for each possible assignment
assignment_features = []
for task in pending_tasks:
for worker in available_workers:
features = {
'task_type': task['type'],
'task_priority': task['priority'],
'task_location': task['zone'],
'worker_id': worker['id'],
'worker_skill_level': worker['skills'].get(task['type'], 0),
'worker_current_zone': worker['location'],
'worker_fatigue_score': self.calculate_fatigue(worker),
'distance_to_task': self.calculate_distance(
worker['location'],
task['zone']
),
'estimated_completion_time': task['estimated_minutes']
}
assignment_features.append(features)
# Get model predictions for assignment quality scores
predictions = self.endpoint.predict(instances=assignment_features)
# Select optimal assignments (solving assignment problem)
assignments = self.solve_assignment_problem(
predictions.predictions,
pending_tasks,
available_workers
)
return assignments
def calculate_fatigue(self, worker):
"""Calculate worker fatigue based on recent activity"""
hours_worked = worker['hours_today']
tasks_completed = worker['tasks_today']
return min(1.0, (hours_worked / 8.0) + (tasks_completed / 50.0))
def solve_assignment_problem(self, scores, tasks, workers):
"""
Use scores to create optimal task assignments
Implements Hungarian algorithm or similar optimization
"""
# Implementation of assignment optimization
# Returns list of (task_id, worker_id) pairs
pass
Gemini for understanding context and priorities adds intelligence that goes beyond numerical optimization:
def contextual_priority_adjustment(task_queue):
"""
Use Gemini to understand task context and adjust priorities
"""
model = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
# Gather context from various sources
context = {
'current_tasks': task_queue,
'active_orders': get_active_orders(),
'customer_messages': get_recent_customer_inquiries(),
'manager_notes': get_shift_supervisor_notes()
}
prompt = f"""
You are an AI agent managing warehouse task prioritization.
Current context:
{json.dumps(context, indent=2)}
Analyze this situation and provide:
1. Any tasks that should be escalated based on customer urgency or business impact
2. Tasks that can be safely delayed
3. Suggested task groupings for efficiency (e.g., pick these orders together)
4. Worker assignments considering stated preferences or capabilities
Consider factors like:
- Customer SLAs and VIP status
- Order deadlines
- Product perishability
- Worker specializations mentioned in notes
- Operational efficiency
Return structured recommendations with reasoning.
"""
response = model.generate_content(prompt)
return parse_priority_recommendations(response.text)
Dynamic resource allocation responds to changing conditions in real-time, redistributing workers as priorities shift.
C. Visual Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control has traditionally required human inspectors examining products. Gemini's multimodal capabilities enable automated, consistent inspection at scale.
class QualityInspectionAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.model = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
self.inspection_history = []
def inspect_product(self, product_images, product_specs):
"""
Multi-angle product inspection using Gemini vision
"""
# Prepare image parts
image_parts = [
Part.from_uri(mime_type="image/jpeg", uri=img_uri)
for img_uri in product_images
]
inspection_prompt = f"""
Perform quality inspection on this product:
Product Specifications:
{json.dumps(product_specs, indent=2)}
Inspect the provided images for:
1. **Physical Damage**: scratches, dents, cracks, deformation
2. **Label Quality**: readability, correct placement, no smearing
3. **Packaging Integrity**: seals intact, no tears, proper closure
4. **Completeness**: all expected components visible
5. **Color Accuracy**: matches specification (if applicable)
6. **Dimensional Accuracy**: appears correct size/proportions
For each category:
- Status: PASS / FAIL / WARNING
- Confidence: 0-100%
- Details: specific observations
- Location: where in images the issue appears
Return structured JSON inspection report.
"""
response = self.model.generate_content(image_parts + [inspection_prompt])
inspection_result = self.parse_inspection_result(response.text)
self.log_inspection(inspection_result)
return inspection_result
def defect_classification(self, defect_image):
"""
Detailed defect analysis and classification
"""
defect_part = Part.from_uri(
mime_type="image/jpeg",
uri=defect_image
)
classification_prompt = """
Analyze this product defect in detail:
1. Defect Type: (scratch, dent, crack, discoloration, misalignment, etc.)
2. Severity: (CRITICAL - cannot ship, MAJOR - customer return likely, MINOR - cosmetic only)
3. Likely Cause: (manufacturing, shipping damage, handling, storage)
4. Root Cause Category: (supplier quality, internal handling, carrier damage)
5. Recommended Action: (reject, accept with discount, rework, return to supplier)
6. Prevention Suggestions: specific steps to prevent recurrence
Provide detailed analysis with confidence levels.
"""
response = self.model.generate_content([defect_part, classification_prompt])
return response.text
def batch_compliance_check(self, batch_images, compliance_requirements):
"""
Check entire batch against compliance requirements
"""
prompt = f"""
Review this batch of products for compliance with:
{compliance_requirements}
Check each image for:
- Required labels and certifications present
- Proper packaging meeting regulations
- Correct product markings
- Safety seals intact
- Regulatory compliance indicators
Identify:
1. Compliant items (percentage)
2. Non-compliant items with specific violations
3. Questionable items needing human review
4. Batch-level compliance status (PASS/FAIL)
Return summary with item-level details.
"""
image_parts = [Part.from_uri("image/jpeg", uri) for uri in batch_images]
response = self.model.generate_content(image_parts + [prompt])
return self.parse_compliance_report(response.text)
D. Intelligent Document Processing
Warehouses process thousands of documents daily—bills of lading, commercial invoices, packing slips, customs forms. Gemini automates this entirely.
class DocumentProcessingAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.model = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
def process_shipping_document(self, document_image_or_pdf):
"""
Extract all relevant information from shipping documents
"""
doc_part = Part.from_uri(
mime_type="application/pdf", # or image/jpeg
uri=document_image_or_pdf
)
extraction_prompt = """
Extract all information from this shipping document:
Required fields:
- Shipper name and address
- Consignee name and address
- Carrier and tracking number
- BOL or AWB number
- Ship date and expected delivery
- Item descriptions and quantities
- Weights and dimensions
- Special handling instructions
- Declared value
- Incoterms
Additional analysis:
- Document type identification
- Completeness assessment (any missing required fields)
- Data quality issues (illegible, inconsistent)
- Red flags (mismatches, unusual values)
Return structured JSON with extracted data and analysis.
"""
response = self.model.generate_content([doc_part, extraction_prompt])
extracted_data = json.loads(response.text)
# Validate against database
validation_result = self.validate_shipment_data(extracted_data)
return {
'extracted_data': extracted_data,
'validation': validation_result,
'requires_human_review': validation_result['issues_found']
}
def validate_shipment_data(self, extracted_data):
"""
Cross-reference extracted data with purchase orders and inventory
"""
prompt = f"""
Validate this extracted shipment data against our records:
Extracted Data:
{json.dumps(extracted_data, indent=2)}
Purchase Order Data:
{json.dumps(self.get_matching_po(extracted_data['po_number']), indent=2)}
Check for:
1. Quantity matches PO
2. SKUs match PO
3. Shipper matches expected supplier
4. Delivery address matches our warehouse
5. Special instructions match PO requirements
Flag any discrepancies with severity level and recommended action.
Return validation report with PASS/FAIL status and detailed findings.
"""
response = self.model.generate_content(prompt)
return json.loads(response.text)
def handle_exceptions(self, discrepancy_report):
"""
Intelligent exception handling with recommended resolutions
"""
prompt = f"""
A discrepancy was found in shipment processing:
{json.dumps(discrepancy_report, indent=2)}
Based on the type and severity of discrepancy:
1. Can this be automatically resolved? If yes, how?
2. Does this require human review? Which role?
3. Should shipment be accepted, rejected, or held?
4. What documentation is needed?
5. Who needs to be notified?
6. What's the recommended resolution path?
Consider:
- Business rules for acceptance tolerances
- Cost of rejection vs acceptance
- Customer impact
- Supplier relationship
Provide decision recommendation with confidence level and reasoning.
"""
response = self.model.generate_content(prompt)
return self.route_exception(response.text)
E. Predictive Maintenance
Equipment downtime can halt entire warehouse operations. Predictive maintenance using Vertex AI and Gemini prevents failures before they occur.
class PredictiveMaintenanceAgent:
def __init__(self, equipment_model_endpoint):
self.endpoint = aiplatform.Endpoint(equipment_model_endpoint)
self.gemini = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
def monitor_equipment_health(self, equipment_id):
"""
Continuous monitoring with predictive failure detection
"""
# Get sensor data
sensor_data = self.get_sensor_readings(equipment_id)
# Vertex AI model predicts failure probability
prediction = self.endpoint.predict(instances=[{
'equipment_id': equipment_id,
'vibration_level': sensor_data['vibration'],
'temperature': sensor_data['temperature'],
'operating_hours': sensor_data['hours'],
'load_cycles': sensor_data['cycles'],
'maintenance_history': sensor_data['last_service_days']
}])
failure_probability = prediction.predictions[0]['failure_risk']
if failure_probability > 0.7:
# High risk - generate detailed analysis with Gemini
maintenance_plan = self.generate_maintenance_plan(
equipment_id,
sensor_data,
failure_probability
)
return maintenance_plan
return {'status': 'normal', 'failure_risk': failure_probability}
def generate_maintenance_plan(self, equipment_id, sensor_data, risk_score):
"""
Use Gemini to create comprehensive maintenance plan
"""
# Gather all relevant context
maintenance_history = self.get_maintenance_logs(equipment_id)
technician_notes = self.get_recent_notes(equipment_id)
similar_failures = self.query_similar_equipment_failures()
prompt = f"""
URGENT: Predictive maintenance alert for {equipment_id}
Current Situation:
- Failure Risk Score: {risk_score * 100:.1f}%
- Sensor Readings: {json.dumps(sensor_data, indent=2)}
Historical Context:
- Maintenance History: {maintenance_history}
- Recent Technician Notes: {technician_notes}
- Similar Equipment Failures: {similar_failures}
Create a detailed maintenance plan:
1. **Failure Mode Analysis**: What specific failure is predicted?
2. **Urgency Assessment**: How soon should maintenance occur?
3. **Recommended Actions**: Step-by-step maintenance procedure
4. **Parts Needed**: Specific components likely required
5. **Estimated Downtime**: How long will equipment be offline?
6. **Workaround Options**: Can operations continue with reduced capacity?
7. **Scheduling Recommendation**: Best time window for maintenance
8. **Preventive Measures**: How to prevent recurrence
Consider:
- Current warehouse workload and peak times
- Parts availability and lead times
- Technician scheduling
- Impact on operations
- Cost of preventive vs reactive maintenance
Provide actionable plan with confidence levels and alternative approaches.
"""
response = self.gemini.generate_content(prompt)
# Parse and create work orders
plan = json.loads(response.text)
self.create_maintenance_work_order(equipment_id, plan)
self.notify_stakeholders(plan)
return plan
def analyze_failure_patterns(self):
"""
Learn from failures to improve predictions
"""
failures = self.get_historical_failures()
pattern_prompt = f"""
Analyze these equipment failure records to identify patterns:
{json.dumps(failures, indent=2)}
Identify:
1. Common failure modes
2. Leading indicators (sensor patterns that preceded failures)
3. Seasonal or operational patterns
4. Manufacturer or model-specific issues
5. Maintenance practice gaps
Recommend:
1. Improved monitoring parameters
2. Adjusted maintenance schedules
3. Spare parts inventory optimization
4. Training needs for maintenance team
5. Equipment replacement priorities
Provide actionable insights for operational improvement.
"""
analysis = self.gemini.generate_content(pattern_prompt)
return analysis.text
F. Conversational AI for Operations
Gemini enables natural language interaction with warehouse systems, making technology accessible to all workers.
class WarehouseAssistantAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.model = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
self.conversation_history = []
def handle_worker_query(self, worker_id, query, context=None):
"""
Process natural language queries from warehouse workers
"""
# Get worker context
worker_info = self.get_worker_info(worker_id)
current_location = worker_info['current_zone']
assigned_tasks = worker_info['tasks']
# Build context-aware prompt
system_context = f"""
You are an AI assistant helping warehouse worker #{worker_id}.
Worker Context:
- Name: {worker_info['name']}
- Current Location: {current_location}
- Assigned Tasks: {assigned_tasks}
- Skill Level: {worker_info['skill_level']}
- Today's Tasks Completed: {worker_info['tasks_completed_today']}
You have access to:
- Inventory database
- Order management system
- Equipment status
- Layout and location information
- Training materials and procedures
Provide helpful, concise responses. If the worker needs to perform an action:
1. Guide them step-by-step
2. Reference their current location
3. Provide safety reminders when relevant
4. Update systems automatically when possible
Always be supportive and assume positive intent.
"""
# Combine with conversation history
messages = self.conversation_history[-5:] + [
f"Worker: {query}"
]
full_prompt = f"{system_context}\n\nConversation:\n" + "\n".join(messages)
response = self.model.generate_content(full_prompt)
# Check if response requires system actions
if self.requires_system_action(response.text):
self.execute_system_actions(response.text, worker_id)
# Update conversation history
self.conversation_history.append(f"Worker: {query}")
self.conversation_history.append(f"Assistant: {response.text}")
return response.text
def voice_activated_operations(self, audio_input, worker_id):
"""
Process voice commands from workers
"""
# Note: Gemini can process audio directly in multimodal mode
audio_part = Part.from_data(
mime_type="audio/wav",
data=audio_input
)
prompt = """
Transcribe and interpret this voice command from a warehouse worker.
Common commands include:
- "Where is SKU [number]?"
- "Mark current task complete"
- "What's my next task?"
- "Report damaged item"
- "Request assistance"
- "How many of [SKU] do we have?"
Respond with:
1. Transcribed command
2. Interpreted intent
3. Required system action
4. Worker-friendly response (for text-to-speech)
"""
response = self.model.generate_content([audio_part, prompt])
# Process and execute
command_info = json.loads(response.text)
result = self.execute_voice_command(command_info, worker_id)
return {
'transcription': command_info['transcription'],
'response': command_info['worker_response'],
'action_taken': result
}
Architecture and Integration
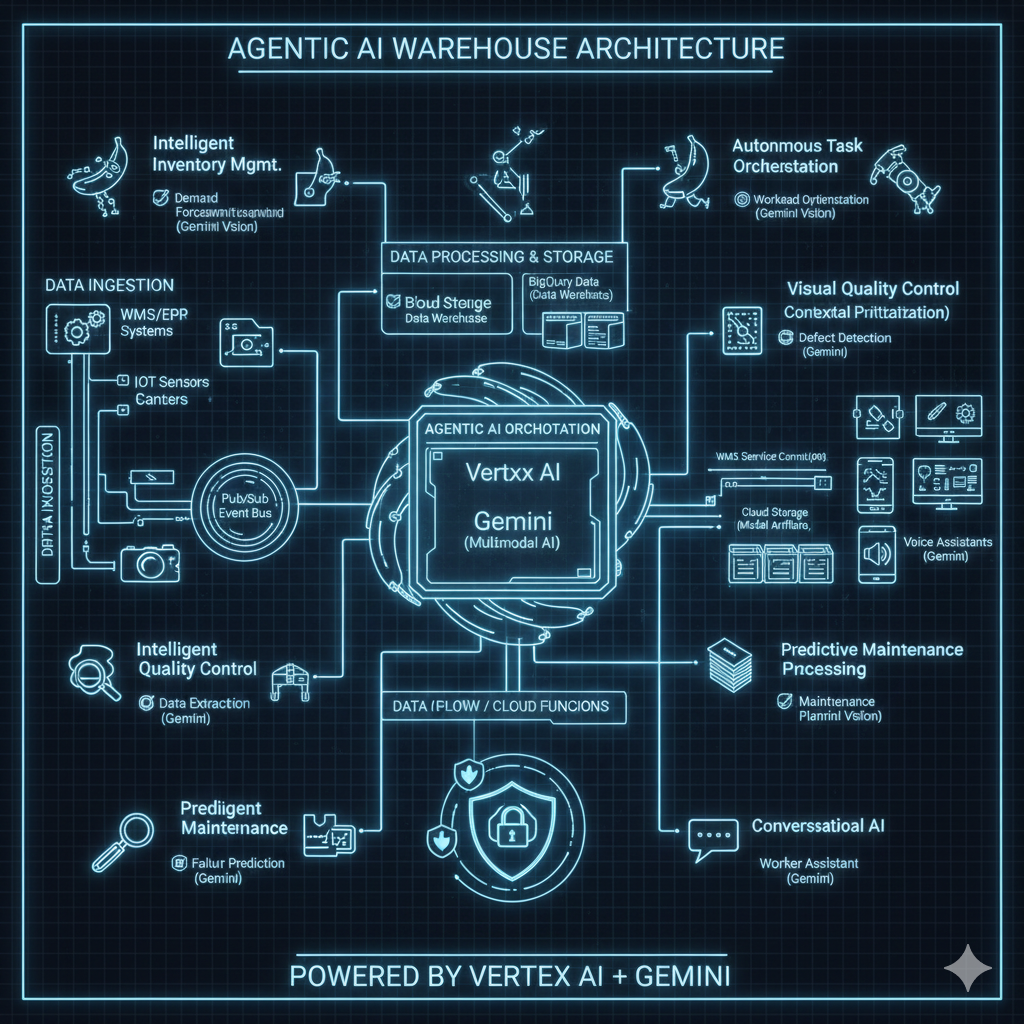
Building an agentic AI system requires thoughtful integration with existing warehouse infrastructure. Here's a reference architecture:
# Sample architecture showing integration patterns
class WarehouseAIArchitecture:
"""
Reference architecture for Vertex AI + Gemini warehouse integration
"""
def __init__(self, project_id):
self.project_id = project_id
# Initialize Google Cloud clients
self.bigquery_client = bigquery.Client()
self.storage_client = storage.Client()
self.pubsub_publisher = pubsub_v1.PublisherClient()
self.aiplatform_client = aiplatform.gapic.PredictionServiceClient()
# Initialize Gemini
vertexai.init(project=project_id, location='us-central1')
self.gemini = GenerativeModel('gemini-1.5-pro')
def setup_data_pipeline(self):
"""
Configure data flow from WMS to AI systems
"""
# 1. Real-time events via Pub/Sub
topic_path = self.pubsub_publisher.topic_path(
self.project_id,
'warehouse-events'
)
# 2. Batch data in BigQuery
dataset_ref = self.bigquery_client.dataset('warehouse_analytics')
# 3. Model artifacts in Cloud Storage
bucket = self.storage_client.bucket(f'{self.project_id}-ml-models')
# 4. Streaming data pipeline (example)
pipeline = {
'sources': [
'wms_database', # CDC from WMS
'iot_sensors', # Equipment sensors
'camera_feeds', # Visual data
'erp_system' # Order and inventory data
],
'processing': [
'pubsub_ingestion',
'dataflow_transformation',
'bigquery_loading',
'real_time_prediction'
],
'destinations': [
'vertex_ai_endpoints',
'gemini_api',
'operational_dashboard'
]
}
return pipeline
def deploy_agent_system(self):
"""
Deploy complete agentic AI system
"""
# Deploy Vertex AI models
forecast_endpoint = self.deploy_forecast_model()
task_optimizer_endpoint = self.deploy_task_optimizer()
maintenance_endpoint = self.deploy_maintenance_predictor()
# Configure Gemini access
gemini_config = {
'model': 'gemini-1.5-pro',
'temperature': 0.1, # Low for operational consistency
'max_output_tokens': 2048
}
# Create agent orchestrator
orchestrator = AgentOrchestrator(
vertex_endpoints={
'forecast': forecast_endpoint,
'task_optimization': task_optimizer_endpoint,
'maintenance': maintenance_endpoint
},
gemini_model=self.gemini,
event_bus=self.pubsub_publisher
)
return orchestrator
def integrate_with_wms(self, wms_api_config):
"""
Bidirectional integration with WMS
"""
class WMSIntegration:
def __init__(self, api_config):
self.api_base = api_config['url']
self.auth_token = api_config['token']
def get_inventory_realtime(self):
"""Pull current inventory from WMS"""
response = requests.get(
f"{self.api_base}/inventory",
headers={'Authorization': f'Bearer {self.auth_token}'}
)
return response.json()
def update_task_assignments(self, assignments):
"""Push AI-generated task assignments to WMS"""
response = requests.post(
f"{self.api_base}/tasks/assign",
json=assignments,
headers={'Authorization': f'Bearer {self.auth_token}'}
)
return response.status_code == 200
def subscribe_to_events(self, callback):
"""Subscribe to WMS events via webhook"""
webhook_url = f"https://{self.project_id}.cloudfunctions.net/wms-events"
requests.post(
f"{self.api_base}/webhooks/subscribe",
json={'url': webhook_url, 'events': ['*']},
headers={'Authorization': f'Bearer {self.auth_token}'}
)
return WMSIntegration(wms_api_config)
Data pipeline architecture typically flows:
Ingestion Layer: Pub/Sub topics receive real-time events from WMS, IoT sensors, cameras
Processing Layer: Dataflow transforms and enriches data, Cloud Functions handle event-driven logic
Storage Layer: BigQuery stores analytical data, Cloud Storage holds model artifacts and media
ML Layer: Vertex AI endpoints serve predictions, Gemini provides reasoning and generation
Application Layer: Cloud Run hosts agent services, Firebase provides mobile interfaces
Security and access control leverages Google Cloud's IAM:
Service accounts with minimal permissions for each component
VPC Service Controls to isolate sensitive data
Cloud Armor for API protection
Encryption at rest and in transit
Audit logging for compliance
Real-World Benefits and ROI
Organizations implementing Vertex AI and Gemini for warehouse operations typically see:
Operational cost reduction: 25-40% reduction in labor costs through optimized task assignment and 15-20% reduction in inventory holding costs through improved forecasting.
Accuracy improvements: Inventory accuracy improves from typical 95% to 99.5%+, order picking errors drop by 60-80%, and quality defect detection improves to near 100% consistency.
Speed and throughput gains: Order fulfillment time reduces by 30-50%, receiving and put-away processes speed up by 40%, and peak season capacity increases by 50-100% without proportional staffing increases.
Reduced implementation time: Vertex AI's managed services eliminate months of infrastructure setup. AutoML enables model development in days rather than months. Pre-trained Gemini requires no training for many use cases.
Scalability advantages: Cloud-native architecture scales automatically from pilot to enterprise-wide deployment. Processing capacity expands instantly during peak demand. Geographic expansion deploys in new regions within days.
Total cost of ownership: While initial investment includes Google Cloud fees and integration costs, typical ROI appears within 6-12 months through labor savings, error reduction, and throughput improvements. Ongoing costs are predictable and scale with usage.
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Assessment and Pilot Project Selection (4-6 weeks)
Audit current systems and identify integration points
Select high-impact pilot (typically inventory forecasting or quality inspection)
Establish success metrics and baseline measurements
Form cross-functional team (operations, IT, data science)
Phase 2: Data Preparation and Model Training in Vertex AI (6-8 weeks)
Extract and clean historical data from WMS/ERP
Design BigQuery schemas for analytical data
Build initial forecasting or classification models using AutoML
Deploy first model endpoint
Validate predictions against held-out test data
Phase 3: Gemini Integration for Multimodal Capabilities (4-6 weeks)
Identify use cases requiring unstructured data processing
Develop prompt templates for consistency
Build integration layer connecting Gemini to operational systems
Test on sample documents, images, or conversations
Implement safety and quality controls
Phase 4: Deployment and Monitoring (8-12 weeks)
Deploy agents in limited production scope
Establish monitoring dashboards (Cloud Monitoring, custom metrics)
Implement feedback loops for continuous improvement
Train warehouse staff on new AI-assisted workflows
Document procedures and troubleshooting guides
Phase 5: Scaling and Optimization (Ongoing)
Expand successful pilots to additional use cases
Retrain models with production data
Optimize costs through right-sizing and caching
Roll out to additional facilities
Develop advanced agents with multi-step reasoning
Change management and workforce enablement are critical. Success requires:
Clear communication about AI augmenting (not replacing) workers
Hands-on training sessions demonstrating practical benefits
Champions among warehouse staff who advocate for adoption
Feedback mechanisms allowing workers to report issues or suggestions
Celebrating early wins to build momentum
Future Capabilities on the Horizon
Google Cloud's AI roadmap promises even more powerful capabilities:
Upcoming Vertex AI and Gemini features include longer context windows (enabling analysis of entire day's operations), improved multi-step reasoning (complex decision chains), enhanced code generation (automated workflow creation), and real-time video understanding (continuous monitoring without pre-processing).
Fully autonomous warehouse operations will emerge as agents handle increasingly complex decisions with minimal human oversight. Facilities may run lights-out during off-peak hours while maintaining full operational capability.
Advanced human-AI collaboration models will create true partnership between workers and agents. Workers focus on exception handling, complex problem-solving, and customer interactions while AI manages routine optimization and coordination.
Edge AI deployment brings processing to warehouse locations, reducing latency for time-critical decisions and enabling operation during network disruptions. Edge TPUs run models locally while syncing with cloud for training and updates.
Sustainability and energy optimization becomes increasingly important. AI agents optimize energy consumption, routing electric vehicles efficiently, adjusting lighting and climate control dynamically, and selecting carrier options with lower carbon footprints.
Conclusion and Call-to-Action
The warehouse of tomorrow isn't some distant vision—it's being built today with Vertex AI and Gemini. These technologies transform warehouses from reactive cost centers into proactive competitive advantages. Agentic AI doesn't just make operations faster; it makes them smarter, continuously learning and adapting to deliver outcomes that static automation could never achieve.
Google Cloud's approach offers distinct advantages: enterprise-grade infrastructure with proven reliability, multimodal capabilities that process any data type, managed services that accelerate deployment, and seamless integration with existing systems. The combination of Vertex AI's robust ML platform with Gemini's advanced reasoning creates agents that truly understand your operations and make intelligent decisions in real-time.
Next steps for getting started:
Assess your readiness: Evaluate data quality, system integration capabilities, and organizational buy-in
Identify a pilot project: Choose a high-value, well-defined use case (inventory forecasting is often ideal)
Engage with Google Cloud: Contact your account team or visit cloud.google.com/vertex-ai to explore resources
Build a small team: Combine operational expertise with technical capability
Start small, think big: Pilot quickly, measure rigorously, scale systematically
The competitive landscape is shifting rapidly. Early adopters of agentic AI are already seeing transformative results. The question isn't whether AI will revolutionize warehouse operations—it's whether your organization will lead the transformation or struggle to catch up.
Resources for Getting Started:
Vertex AI Documentation: cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs
Gemini API Guide: cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/
Google Cloud Architecture Center: Warehouse use cases and reference architectures
Contact: Reach out to Google Cloud sales for pilot program opportunities
The warehouse of tomorrow is being built today. With Vertex AI and Gemini, your operations can lead the way.
Ready to transform your warehouse operations with agentic AI? Contact Google Cloud to discuss a pilot project tailored to your specific needs and challenges.



